The Science Behind Seasonal Eating in the Mediterranean Diet
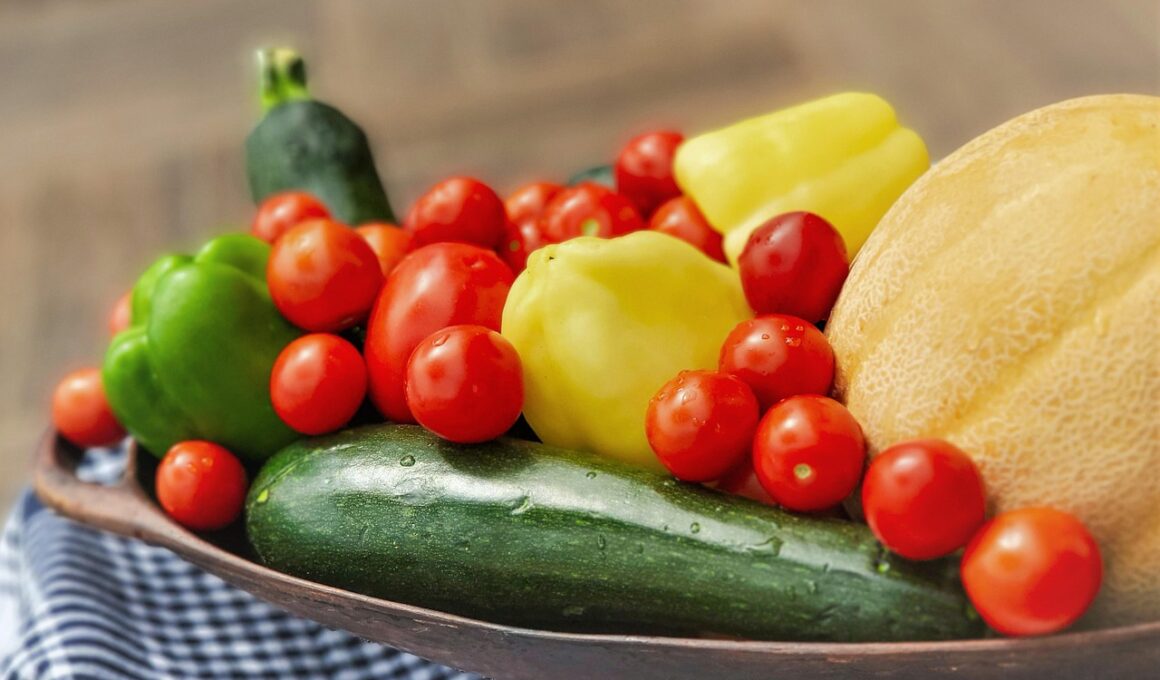
The Mediterranean Diet is well-known for its rich flavors and numerous health benefits. A fundamental principle of this diet is seasonal eating, which emphasizes the use of fresh, locally sourced ingredients. Seasonal foods boast higher nutrient levels and superior taste. When these foods are harvested at their peak, they provide a wide array of vitamins and minerals, promoting overall health. Studies have shown that seasonal fruits and vegetables contain more antioxidants, which play a crucial role in protecting the body from aging and chronic diseases. The Mediterranean region, with its diverse climates, offers a unique variety of seasonal foods. This variety ensures that those following the diet have access to numerous options throughout the year, fostering a balanced intake of nutrients. Eating according to the seasons also supports local farmers and economies, encouraging sustainable agricultural practices. Seasonal eating aligns well with traditions in Mediterranean cultures, where meals include what is available from local markets. This creates a strong connection to the environment and seasons, further enhancing the dining experience. Fresh, seasonal ingredients lead to greater culinary creativity and joy in preparing meals.
Incorporating seasonal foods into the Mediterranean diet brings several health advantages. Firstly, seasonal produce is often more affordable, as it is harvested during peak times. This affordability encourages individuals and families to fill their plates with a diverse range of fruits and vegetables. Additionally, when you consume produce in season, you may enjoy better taste, as flavors are more vibrant. For example, ripe tomatoes in summer are sweet and juicy. Furthermore, buying seasonal foods also promotes sustainability. This is an integral aspect of the Mediterranean lifestyle, reflecting a commitment to the environment. By choosing locally grown ingredients, you’re reducing your carbon footprint associated with transportation. Moreover, seasonal eating fosters a deeper appreciation for the changing landscape of food availability. It connects individuals and families to the agricultural cycles of their regions and encourages gratitude for the seasons. Furthermore, integrating various seasonal foods into one’s diet can aid in maintaining a healthy weight, as seasonal produce is low in calories and high in fiber. Embracing this dietary approach can lead to better overall nutrition for individuals and families alike.
The Role of Fruits in the Seasonal Mediterranean Diet
Fruits form a significant part of the Mediterranean diet, especially when consumed in season. Each season presents a unique selection that offers various health benefits. For instance, citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits are prominent in winter, providing essential vitamin C to support the immune system. These fruits combat cold and flu symptoms that often accompany the seasons. In spring, berries such as strawberries and blueberries emerge. They are rich in antioxidants and have anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to heart health and better cognition. Summer brings the arrival of stone fruits like peaches and plums, which are not only delicious but also hydrating due to their high-water content. These fruits help maintain hydration during warm months. Finally, fall introduces apples and pears, excellent sources of fiber that promote digestive health. Each of these fruits thrives in specific climates, encouraging a diverse dietary intake throughout the year. Additionally, they can be incorporated into various dishes, enhancing the versatility of Mediterranean cuisine. This shift in focus from processed foods to whole fruits improves nutrition and overall health.
Vegetables play a crucial role in the Mediterranean diet, particularly when enjoyed in season. Seasonal vegetables are typically harvested at their peak maturity, which means they offer enhanced flavor and nutrition. For example, leafy greens such as kale and chard are abundant during spring, providing vitamins A, C, and K that are vital for overall health. Summer brings a bounty of vegetables like zucchini and tomatoes, along with eggplant, which can be enjoyed grilled, roasted, or in savory ratatouille. These dishes not only heighten culinary creativity but also promote health. Furthermore, root vegetables like carrots and beets are staples in winter. They are nutrient-dense and provide essential carbohydrates for energy. Seasonal vegetables encourage a colorful plate, which helps ensure a variety of nutrients. Different colors indicate the presence of various phytonutrients, and consuming a rainbow of vegetables can bolster immune function and reduce inflammation. Additionally, buying seasonal and local vegetables supports farming communities and encourages sustainable practices. Incorporating seasonal vegetables regularly in meals can enhance flavor profiles and foster a more healthful approach to eating.
Grains and Legumes in Seasonal Eating
Grains and legumes form the backbone of the Mediterranean diet, providing essential nutrients while remaining seasonally based. Whole grains, such as farro, barley, and oats, are often harvested in late summer and early fall. They provide complex carbohydrates, aiding in energy longevity and promoting digestive health thanks to their high fiber content. These grains also serve as a source of important vitamins and minerals, offering fuel for daily activities. Additionally, legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and beans are consumed year-round, but their peak season benefits include a fresh and more vibrant flavor. Rich in protein, they provide an excellent meat alternative for plant-based eaters. Many Mediterranean recipes celebrate the versatility of legumes, allowing them to shine in dishes like hummus and bean salads. By incorporating these grains and legumes seasonally, individuals can enjoy fresher and tastier meals. Moreover, this practice is more sustainable and environmentally friendly, as local farmers can supply what is grown in a particular season. Engaging with seasonal grains enriches diets, showcasing diverse culinary traditions within the Mediterranean lifestyle.
The Mediterranean diet promotes moderate consumption of dairy, particularly in its seasonal eating practices. Choosing dairy products that align with seasonal availability can enhance flavor and nutrition. For instance, fresh goat cheese or sheep’s milk yogurt is often more flavorful during warmer months. Local dairies that follow traditional practices offer products that reflect the season. These cheeses and yogurts can be enjoyed with seasonal vegetables or fruits, creating delightful dishes that resonate with Mediterranean culture. Additionally, incorporating seasonal dairy supports local economies and sustainable farming practices. In early spring, you can savor flavorful cheeses made with milk from goats that have grazed on fresh pasture. Furthermore, dairy contains healthy fats, protein, and calcium, contributing to overall health. Research indicates that incorporating moderate amounts of dairy can boost bone density and promote gut health. By prioritizing seasonal dairy options, individuals can manage portion sizes and savor the mouthfeel of fresh products. Embracing local dairy consumption enriches the Mediterranean diet by allowing the flavors of the season to shine, creating delicious and nutritious meals that support overall well-being.
Benefits of Herbal Seasoning
Herbs and spices are crucial in the Mediterranean diet, enhancing flavors and providing health benefits. Many of these herbs flourish during specific seasons, allowing cooks to incorporate fresh varieties into their dishes. For instance, basil and oregano are in their prime during the summer. These herbs not only provide aromatic qualities to meals but are also known for their potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Thyme and rosemary thrive in warmer weather, infusing dishes with rich flavors and beneficial oils. In the fall, sage and parsley become more abundant, offering a unique flavor profile to seasonal meals. Using fresh herbs can encourage more significant vegetable intake, as they make dishes more appealing. Culinary creativity also expands when herbs are at their freshest, inspiring new recipes that embrace the season. Furthermore, the incorporation of herbs aligns closely with the Mediterranean philosophy, emphasizing natural ingredients. Studies suggest that consuming herbs not only enhances flavor but can also reduce overall sodium intake, which plays a role in heart health. Engaging with seasonal herbs enriches the diet, elevating meals while imparting numerous health advantages.
In conclusion, embracing seasonal eating within the Mediterranean diet unlocks numerous health and taste benefits. Seasonal foods promote better nutrition, support local economies, and connect individuals to their environment. The distinct flavors of fruits, vegetables, grains, and herbs that align with specific seasons create varied and enjoyable meals throughout the year. This way of life emphasizes the importance of choosing fresh, local produce, leading to a more sustainable dietary approach. Seasonal eating enhances culinary creativity, encouraging new recipes and the joy of cooking with fresh ingredients. Additionally, the Mediterranean diet underscores the benefits of balanced nutrition, rich in whole foods that contribute to well-being. As individuals learn to appreciate the beauty of seasonal ingredients, they strengthen their nutritional knowledge and explore new flavors. This connection fosters a sense of community and respect for the natural cycles of agriculture. Ultimately, adopting a seasonal Mediterranean diet is a celebration of food, culture, and health. By embracing this lifestyle, individuals can lead happier, healthier lives, enriched by the abundance of nature’s offerings in every season.