Can a Healthy Gut Help Prevent Chronic Infections?
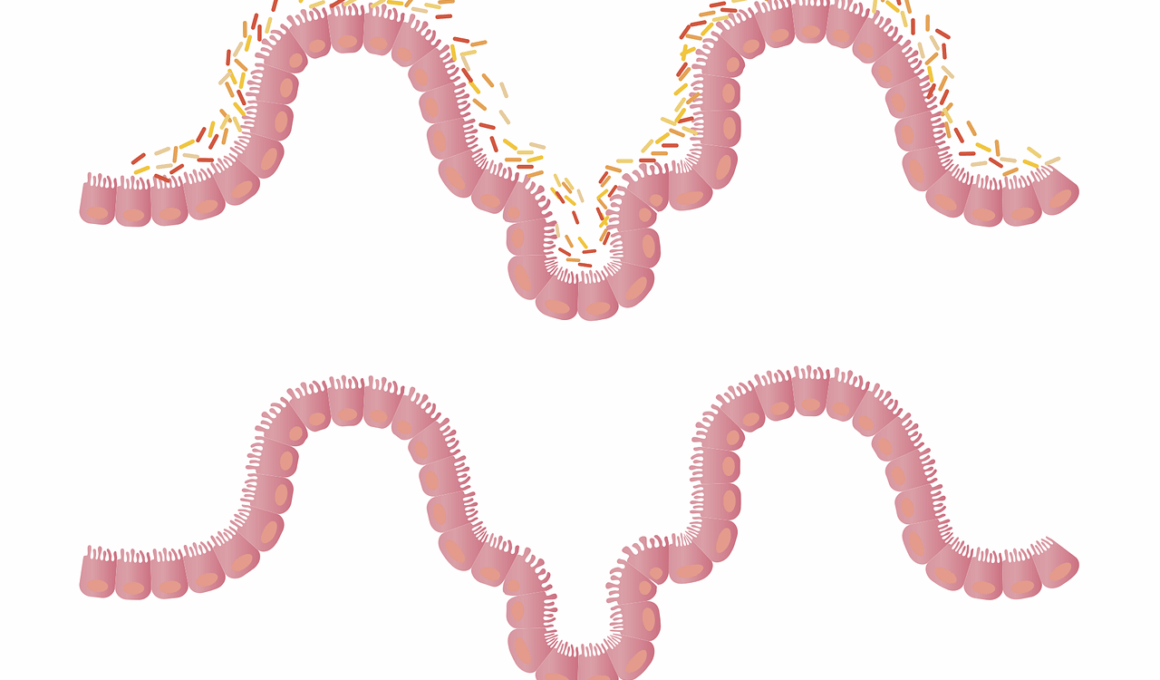
The gut plays a vital role in our overall health, acting as a first line of defense against infections. The gastrointestinal tract is home to trillions of microbes, collectively known as the microbiome, which contribute to our immune system. A balanced gut microbiome produces beneficial compounds, supporting the immune system in combating pathogens. Research shows that an imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to inflammatory conditions, increasing susceptibility to chronic infections. Maintaining gut health through a balanced diet rich in prebiotics and probiotics enhances microbial diversity. Certain foods, including yogurt, sauerkraut, and fiber, are known to promote gut health and, consequently, improve immunity. Furthermore, a healthy gut barrier functions to prevent harmful pathogens from entering the bloodstream. By keeping the gut lining intact and functioning well, the chances of infection can be significantly reduced. Therefore, fostering a diverse gut flora is crucial for immunity and preventing infections. Individuals should aim for diverse diets that include vegetables, fruits, and whole grains to sustain gut health and enhance overall wellness.
Several studies indicate a direct correlation between gut health and immune function. A well-functioning gastrointestinal tract supports the production of various immune cells, including T-cells and antibodies. Research suggests that gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), found in the gut lining, plays a critical role in initiating immune responses. When the gut microbiome is diverse, it educates the immune system, allowing it to respond effectively to harmful pathogens. An unhealthy gut can trigger an overactive immune response or lead to immune tolerance, where the body fails to respond adequately to threats. This is why enhancing gut health is essential in preventing chronic illnesses, such as autoimmune disorders. Recent findings also highlight the importance of gut-brain interactions, where psychological factors may influence gut health and, in turn, immunity. Stress and anxiety can disrupt gut flora, making individuals more prone to infections. Maintaining emotional well-being is thus important for gut health. Integrating mindfulness practices, regular physical activity, and social interactions can positively influence both gut and immune health. Therefore, a holistic approach to wellness is essential for maintaining a resilient immune system and preventing chronic infections.
The food choices we make daily significantly impact our gut microbiome. Diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats may disrupt the balance of gut bacteria. These dietary patterns can lead to dysbiosis, a condition where harmful bacteria outnumber beneficial ones, impairing the gut’s function. Eating a diverse range of nutrient-rich foods can help support a balanced gut microbiome. Fiber-rich foods, such as legumes, fruits, and vegetables, serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria, promoting their growth and activity. Additionally, fermented foods, rich in live cultures, contribute beneficial microorganisms to the gut. These can enhance microbial diversity, promoting better immune responses. When the gut microbiome is well-nourished, it produces short-chain fatty acids that support intestinal health and help regulate inflammation. To foster gut health, individuals should aim for balanced meals that incorporate various food groups, avoiding excessive intake of processed snacks and sweetened beverages. Proper hydration is also crucial for maintaining healthy digestion and gut function. Staying adequately hydrated supports nutrient absorption and helps keep the digestive system functioning effectively. A mindful approach to eating, focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods, can greatly benefit both gut health and immunity.
The Role of Probiotics in Gut Health
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that add to the population of good bacteria in our digestive system. Consuming probiotics can enhance gut health by restoring microbial balance and promoting a healthy gut environment. These live microorganisms are commonly found in fermented foods, such as kefir, yogurt, miso, and kombucha. Scientific research reinforces that probiotics can have a positive impact on specific health conditions, including digestive issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and diarrhea. Some studies even indicate that probiotics may enhance immune responses by training the immune system to react appropriately to pathogens. Regular intake of probiotics can help improve the gut’s barrier function and reduce inflammation. Furthermore, probiotics can help prevent the overgrowth of harmful bacteria in the gut, thereby lowering the risk of chronic infections. Supplement options are also available for those who may not get enough probiotics from their diet. However, it’s important to choose high-quality supplements and consult healthcare professionals when necessary. Incorporating probiotics into one’s daily routine, whether through food or supplements, supports lifelong gut health and enhances immunity.
In addition to probiotics, prebiotics play a crucial role in sustaining gut health. Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria, promoting their growth and activity. Common sources of prebiotics include foods high in fiber, like onions, garlic, bananas, asparagus, and whole grains. Including prebiotic-rich foods in your diet is essential for maintaining a robust microbiome. Studies show that prebiotics can improve gastrointestinal health and enhance immune function by fostering a diverse gut flora. A healthy microbiome not only contributes to better digestion but also supports the production of essential nutrients and vitamins. Furthermore, recent research highlights the potential of prebiotics in regulating inflammation and mitigating the effects of certain food allergies. By consuming a diet that emphasizes both probiotics and prebiotics, individuals can create a nurturing environment for beneficial bacteria to thrive. This dual approach helps to fortify the gut against pathogenic invaders and chronic infections. Understanding the interplay between prebiotics and probiotics is vital for optimizing gut health, ultimately leading to enhanced overall immunity and resistance to infections.
Impact of Lifestyle on Gut Health
Lifestyle factors such as stress, sleep habits, and physical activity also significantly influence gut health. High stress levels can lead to dysbiosis, impacting overall digestive function and immunity. Chronic stress may alter gut motility and enhance gut permeability, allowing harmful substances to enter the bloodstream. Therefore, managing stress through mindfulness practices, yoga, or meditation can improve gut health. Another crucial factor is the quality of sleep. Research shows that insufficient sleep can negatively affect gut microbiota composition, impacting immune responses. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to promote both gut and overall health. Engaging in regular physical exercise is equally important for maintaining a healthy gut. Exercise has been shown to enhance gut motility, promote bacterial diversity, and boost immune function. Activities such as aerobic exercises, strength training, and yoga can all contribute positively to gut health. Thus, a balanced lifestyle that prioritizes stress management, quality sleep, and regular physical activity is essential for optimal gut health and immunity. Taking these steps can significantly reduce the risk of chronic infections and improve overall well-being.
In conclusion, maintaining gut health is a multifaceted approach that significantly impacts the immune system and can help prevent chronic infections. The gut microbiome’s condition is directly linked to our dietary habits, lifestyle choices, and emotional well-being. By focusing on a balanced diet rich in probiotics and prebiotics, individuals can ensure a thriving microbial community that supports immune function. Consuming diverse, nutrient-dense foods enhances microbial diversity, which helps to stimulate immune responses against pathogens. Additionally, making lifestyle changes such as managing stress, prioritizing sleep, and incorporating regular physical activity can further optimize gut health and overall immunity. As science continues to explore the intricate relationship between gut health and immune responses, individuals can begin to appreciate how their choices matter. Taking proactive steps in nurturing gut health fosters resilience against chronic infection risks. Adopting a holistic approach towards diet, lifestyle, and emotional health empowers individuals to lead healthier lives. Ultimately, a robust gut health foundation promotes long-term immunity and contributes to a healthier life overall, reducing the likelihood of chronic infections.
Final Thoughts on Gut Health and Immunity
The discussion around gut health and its influence on immunity underscores the importance of self-care practices. Individuals should prioritize nourishing their gut microbiome through balanced choices. Integrating a variety of prebiotic and probiotic-rich foods into daily meals can significantly enhance gut health. Moreover, being mindful of lifestyle factors and their effects on digestion is equally important. Understanding the significance of sleep, stress management, and physical activity allows individuals to embrace comprehensive approaches to well-being. This may include both dietary adjustments and lifestyle changes designed to promote a balanced microbiome. Listening to one’s body and recognizing signs of digestive distress is essential for maintaining gut health. Awareness of food intolerances and timely interventions can reduce discomfort and enhance overall quality of life. As we continue to learn about the gut’s complexities, it becomes evident that fostering gut health is an ongoing journey. It requires commitment, patience, and the willingness to make informed choices. In summary, investing in gut health promotes not only a resilient immune system but also improves overall health and longevity.