The Role of Celiac Disease in Gut Inflammation Symptoms
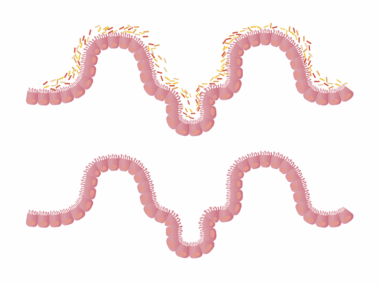
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the gastrointestinal system. It occurs when the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. Gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, triggers an immune response that results in inflammation and damage to the intestinal lining. This inflammation can lead to various symptoms that significantly impact gut health and overall well-being. Distinguishing celiac disease from other gastrointestinal issues is crucial, as it may present similar symptoms to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome or food allergies. Symptoms can vary widely among individuals but often include abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and fatigue, making early diagnosis essential. Proper diagnosis typically involves serological testing and a biopsy of the intestinal tissue to assess for villous atrophy. Once diagnosed, adhering to a strict gluten-free diet can alleviate symptoms and heal the intestinal lining, thus reducing inflammation. Patients experiencing symptoms linked to celiac disease should consult a healthcare professional for comprehensive evaluation and management strategies to ensure long-term health.
Understanding the symptoms associated with celiac disease is essential. Common symptoms encompass digestive issues, including chronic diarrhea and constipation, as well as non-digestive manifestations like dermatitis herpetiformis, which is a skin rash that can be itchy and blistering. Additionally, individuals may experience fatigue, headaches, and joint pain, underscoring the systemic nature of the disease. Many times, symptoms develop after the consumption of gluten-containing foods, drawing a direct line between dietary intake and physical discomfort. The presence of gastrointestinal inflammation can cause malabsorption of nutrients, leading to deficiencies that further exacerbate symptoms. Furthermore, psychological effects such as anxiety and depression may occur due to chronic health challenges. Various lifestyle modifications and nutritional adjustments can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. Education about safe food options and avoidance strategies can empower individuals to manage their condition effectively. If left untreated, celiac disease can result in more severe complications, including osteoporosis, infertility, and an increased risk of gastrointestinal cancers. Thus, recognizing signs of gut inflammation linked to celiac disease is crucial for timely intervention and management.
Connecting Gut Health and Celiac Disease
The intricate connection between gut health and celiac disease highlights why timely assessment and treatment are so significant. In healthy individuals, the gut microbiota plays a crucial role in aiding digestion, supporting the immune system, and maintaining the intestinal barrier. However, in celiac disease patients, gluten consumption disrupts this balance, leading to dysbiosis—an imbalance that can further perpetuate inflammation and exacerbate symptoms. Research has shown potential shifts in microbial communities due to intestinal inflammation present in those with celiac disease. Opportunities exist for new research focusing on how specific probiotics might benefit gut health by restoring this healthy balance. Adopting a gluten-free diet may also alter the gut microbiome positively. Understanding these relationships emphasizes the importance of diet in managing gut inflammation and celiac disease symptoms. Furthermore, educational resources emphasizing meal planning, gluten-free cooking techniques, and the importance of avoiding cross-contamination can enhance patient outcomes. Community support, both online and offline, plays a vital role in offering shared experiences and practical tips, fostering resilience among those living with this condition.
Monitoring symptoms and adhering to dietary guidelines can significantly enhance health outcomes for individuals with celiac disease. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are recommended to assess gut recovery and nutritional status following diagnosis and treatment. Blood tests are also useful for checking antibody levels that indicate whether gluten is still being ingested, even before symptoms reappear. Adopting a gluten-free lifestyle requires diligence in food choices, often necessitating reading labels meticulously and preparing meals from scratch to avoid hidden gluten sources. Seeking out support groups can also provide essential resources, share cooking tips, and create a community for those managing the daily challenges of celiac disease. In this journey, individuals might discover beneficial alternatives and gluten-free grains like quinoa, rice, and corn that can diversify their meals while ensuring that they meet their dietary requirements. Engaging in regular conversations about health and circulating information about gluten-free diets can cultivate awareness and inform others about the complexities of living with celiac disease. This knowledge not only empowers individuals directly affected but can also extend understanding to friends, family, and the wider community.
Long-Term Impacts of Celiac Disease on Gut Health
Over time, consistent inflammation due to untreated celiac disease can result in irreversible damage to the small intestine. The villi, tiny finger-like projections responsible for nutrient absorption, can become blunted or flattened, leading to malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies. Common deficiencies include iron, calcium, vitamin D, and B vitamins, which can complicate existing health issues. In turn, this malnutrition can manifest in broader health conditions, including osteoporosis and anemia, further highlighting the pervasive effects of the condition. Regular screening for associated complications is advised, ensuring that any arising health problems can be managed promptly. Those diagnosed later in life may also face a higher risk of developing secondary health conditions due to previous extended exposure to gluten. It is paramount to understand that healing the gut and restoring balance takes time, requiring patience and dedication to a gluten-free lifestyle. Individuals must also assist their recovery by consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients, engaging in physical activity, and managing stress. These holistic approaches can enhance gut health, supporting overall well-being effectively.
Integrating a comprehensive approach toward health management can bolster recovery for individuals living with celiac disease. Psychological support plays a crucial role, as the emotional burden of managing a chronic disease can impact mental health. Engaging with mental health professionals may be beneficial for individuals who experience anxiety or depression due to their condition. On top of that, stress management techniques can also soothe emotional disturbances and contribute to overall health improvements. Lifestyle adjustments that include regular exercise and mindfulness practices can encourage healthier coping mechanisms. Additionally, engaging nutritionists to ensure proper meal balance can foster adherence to a gluten-free lifestyle, promoting better nutritional choices. Understanding these connections can create a blueprint for symptom management that encompasses physical, mental, and emotional health. Furthermore, establishing a routine following dietary and lifestyle changes can provide structure and stability for individuals navigating their journey with celiac disease. Resources such as workshops, cooking classes, and online webinars can offer valuable knowledge and foster community connections. Empowering those affected not only improves individual outcomes but also increases overall awareness of gut health issues surrounding celiac disease.
The Importance of Research and Awareness
Continued research into celiac disease and its effects on gut inflammation is vital to improve management strategies and patient outcomes. While awareness of gluten-related disorders has increased, celiac disease is still frequently misdiagnosed. Raising awareness about signs and symptoms is essential in primary care settings, allowing for earlier intervention. Engaging with healthcare professionals by providing educational materials can help build a foundation for better understanding. Collaboration between medical professionals and patient advocacy organs can promote early detection and better long-term health outcomes. Moreover, studies focusing on the genetic and environmental factors contributing to celiac disease may unravel more about its mechanisms. Advancements in treatment options, potential new therapies, and the role of the microbiome in gut health continue to be fertile ground for future research. As knowledge grows, therapeutic interventions and nutritional guidelines can evolve, offering more personalized care to patients. Public health initiatives promoting gluten-free awareness can encourage the adoption of healthier eating habits. Such endeavors not only help those diagnosed but create an informed community capable of supporting one another through challenges associated with celiac disease.
In conclusion, understanding the role of celiac disease in gut inflammation symptoms enlightens the broader implications for gut health. Timely awareness, proper diagnosis, and strict adherence to a gluten-free diet are paramount in curbing the symptoms associated with this autoimmune condition. The interconnectedness of gut health dimensions, including the gut microbiome, nutrition, and emotional well-being, reinforces the importance of holistic approaches to management. Promoting research that targets better understanding and innovative treatment options will enhance the quality of life for those affected. Finally, the combined efforts of healthcare providers, advocacy groups, and community support networks can build stronger foundations for sustained health and resilience among celiac disease patients. As knowledge is disseminated, awareness grows, enriching lives through improved gut health outcomes. Empowering individuals to advocate for their health can foster a sense of control over their condition, enhancing overall wellness. By addressing the multifaceted aspects of gut health, comprehensive strategies can emerge that make living with celiac disease manageable. This approach ensures that those affected can navigate life’s challenges with confidence and positivity.