Understanding and Managing Eosinophilic Esophagitis
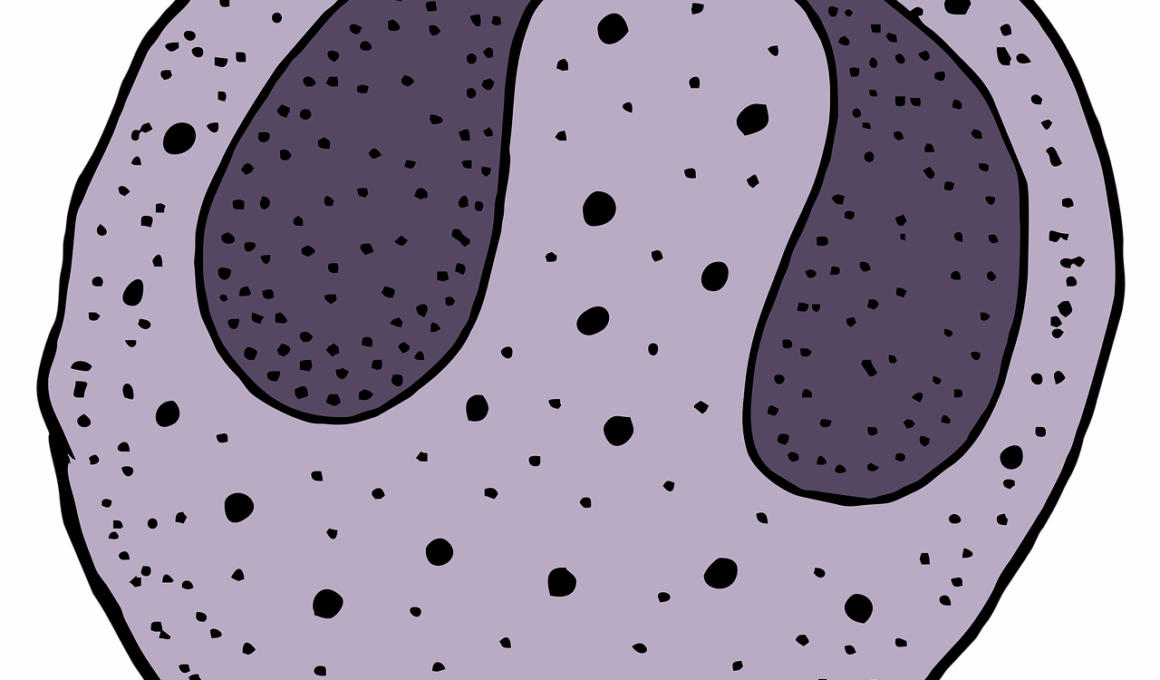
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic immune-mediated condition characterized by an eosinophilic infiltration of the esophagus. This disorder affects individuals across various ages, including children and adults. The symptoms can significantly impact the quality of life, leading to difficulty swallowing, esophageal pain, and food impaction. Clinically, it manifests as inflammation and damage to the esophageal lining, making it essential to understand its etiology. The precise cause of EoE is still under investigation, but it often correlates with allergic conditions and food sensitivities. Foods like dairy, gluten, and nuts have been identified as common allergens that may trigger the condition. Early diagnosis by a gastroenterologist can help manage the symptoms effectively. The evaluation process typically involves esophageal biopsies and allergy testing to determine specific triggers. Furthermore, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing EoE. It’s vital to maintain regular communication with healthcare providers to adapt treatment plans based on individual responses. Patients need to be aware of their dietary restrictions to alleviate symptoms and enhance their overall well-being.
Once diagnosed with eosinophilic esophagitis, patients usually require personalized treatment approaches for effective management. Treatment often begins with dietary interventions aimed at eliminating specific trigger foods. An elimination diet may involve removing common allergens from daily meals for a certain period, followed by a gradual reintroduction to identify the specific offending agents. In some cases, medical therapy may also be required to reduce esophageal inflammation. Topical steroids, such as fluticasone or budesonide, may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. These medications work by reducing inflammation directly in the esophagus. Regular monitoring through endoscopies and biopsies helps gauge the effectiveness of the treatment and guide further actions. Adherence to treatment plans is crucial for minimizing the symptoms associated with EoE and preventing complications such as strictures, which can result from chronic inflammation. Patients may also benefit from collaborating with nutritionists to ensure their dietary needs are met while adhering to food restrictions. It’s vital to adopt a holistic approach that involves both pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies to ensure optimal outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Individuals with eosinophilic esophagitis typically present with various symptoms that can manifest differently between children and adults. In children, common signs may include feeding difficulties, failure to thrive, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Conversely, adults may experience chest pain, difficulty swallowing, or a sensation of food getting stuck in the throat. These symptoms can mimic other gastrointestinal disorders like reflux disease and should therefore be carefully evaluated by a healthcare professional. Diagnosis often requires a combination of clinical assessments, detailed patient history, and endoscopic procedures. Gastroenterologists perform upper endoscopies to visualize the esophagus and obtain tissue biopsies for histological examination. The presence of eosinophils in the esophageal tissue confirms the diagnosis of EoE. Additionally, allergy testing may be necessary to identify other potential triggers. Early recognition of symptoms is crucial as delayed diagnosis and treatment can lead to significant complications. Family physicians should be vigilant in assessing recurrent esophageal symptoms, promoting timely referral to specialists. Continual education about the condition can empower patients and caregivers in recognizing early signs while facilitating prompt evaluation.
In managing eosinophilic esophagitis, it’s essential for patients to adopt specific lifestyle modifications. Dietary management represents a focal point in controlling symptoms and preventing disease exacerbations. besides dietary adjustments, patients may find lifestyle changes beneficial. Maintaining a food diary can help individuals identify patterns related to their symptoms. Documenting food intake along with any symptoms allows for effective correlations to be drawn over time. Additionally, practicing mindful eating, such as slower food consumption and thorough chewing, may decrease the discomfort associated with swallowing. Patients are also advised to stay hydrated and incorporate a balanced diet rich in vitamins while adhering to any restrictions. Beyond diet, regular medical follow-ups are vital to assess esophageal health through endoscopies. Stress management techniques, including meditation and yoga, can also enhance overall well-being. Mental health support should not be overlooked; patients often face emotional struggles due to their dietary limitations and health challenges. Building a support network of family and friends can greatly assist in maintaining morale and motivation throughout the management journey.
Complications of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis can lead to several complications if not managed appropriately. Over time, ongoing esophageal inflammation may cause narrowing or strictures in the esophagus, leading to increased difficulty swallowing and potential food impaction. Strictures, when formed, compromise esophageal motility and can significantly affect nutritional intake. In severe cases, patients may require endoscopic dilation procedures to alleviate symptoms associated with strictures. Beyond physical complications, ongoing EoE can have psychological impacts, including anxiety and depression. Chronic illnesses affecting daily functioning can lead to emotional distress and social isolation. Early intervention is crucial in mitigating these risks, highlighting the importance of routine monitoring. Encouraging communication among patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers can foster a thorough understanding of potential complications. Furthermore, patient education around proper symptom management strategies is vital. Awareness of the need for regular check-ups and the associated procedures can alleviate concerns regarding potential complications. Knowledge is empowering; understanding the complexities of EoE can encourage proactive measures in treatment adherence and lifestyle adjustments to prevent severe outcomes.
Research continues to evolve around eosinophilic esophagitis, aiming to provide better insights into its underlying mechanisms. Scientific studies are investigating genetic predispositions that may increase an individual’s susceptibility to EoE. Advances in biotechnology are also contributing to more precise diagnostic tools, enabling earlier detection and personalized approaches for treatment. Furthermore, clinical trials are examining new therapeutic agents that may offer symptomatic relief for patients who do not respond to conventional treatments or dietary modifications. As medical research progresses, new findings can lead to the development of innovative strategies that target the eosinophilic inflammation in the esophagus effectively. Keeping abreast of the latest advancements in research can greatly benefit both patients and healthcare providers. Patient registries and databases are also being established to track long-term outcomes and treatment success rates. Increased community awareness and advocacy programs play a significant role in improving understanding and support for individuals with EoE. Engaging in ongoing discussions within medical communities can ensure that practices and protocols remain current and effective in addressing this complex disorder.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding eosinophilic esophagitis is crucial for effective management and improving patient quality of life. Comprehensive care must combine dietary management, medical therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Individuals at risk for EoE should be educated about potential symptoms and encouraged to seek medical advice when experiencing recurrent esophageal discomfort. Early diagnosis can facilitate appropriate interventions, significantly lowering the risk of complications. Collaboration among healthcare providers, patients, and families can foster a supportive environment that encourages adherence to management strategies. Access to mental health resources adds another layer of support that acknowledges the emotional challenges faced by those diagnosed with chronic conditions. As research continues to unveil more about the intricacies of EoE, we can anticipate future advancements in both treatment options and improving diagnostic accuracy. Continued education and advocacy remain essential in promoting greater community awareness about eosinophilic esophagitis. Efforts to increase understanding can lead to improved care pathways for affected individuals and encourage societal acceptance of dietary restrictions in social settings. By adopting a multifaceted approach, we can ensure the continued advancement of our understanding and management of EoE.
Key Takeaways:
- Eosinophilic esophagitis is a chronic immune-mediated condition.
- Symptoms differ between children and adults.
- Management includes dietary adjustments and medications.
- Regular follow-up and monitoring are essential.
- Research continues to evolve, improving treatment options.