The Art and Science of Traditional Fermentation in Meat Products
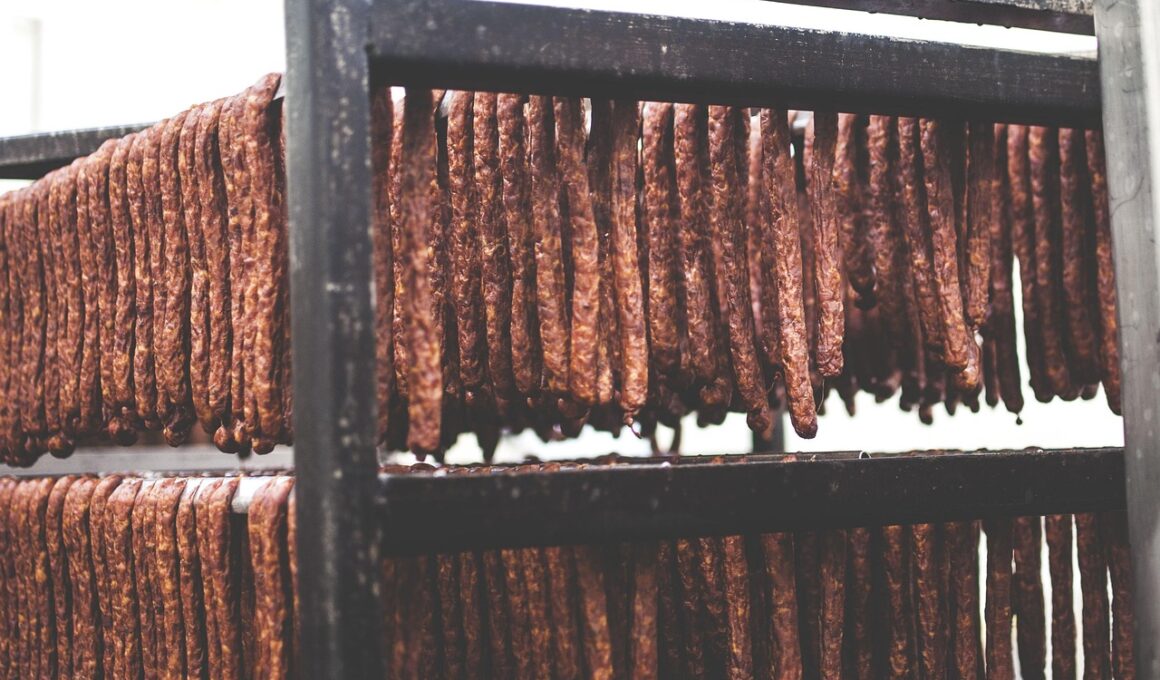
Fermentation has been a vital method for preserving meat and enhancing its flavors across cultures. Through traditional fermentation methods, we can produce various meat products, such as sausages and cured meats. These techniques not only preserve the meat but also contribute to its unique taste and texture. Fermented meat products have a long history, with regional variations that reflect local resources, climate, and culinary preferences. The fermentation process involves beneficial microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, and molds. They metabolize sugars and proteins, leading to a distinctive profile of flavors and aromas. Additionally, fermentation can enhance meat safety by lowering pH and inhibiting harmful bacteria. Important traditional methods include air drying and smoking, both of which have significant impacts on flavor, preservation, and quality. Notably, regions renowned for cured meats, such as Italy and Spain, have perfected these techniques over generations. Through controlled fermentation, essential nutrients can be retained and probiotics introduced, which are beneficial for gut health. Thus, understanding these techniques unveil not only culinary delights but also the science behind food preservation and enrichment.
The Microbial Community in Fermented Meats
The success of traditional fermentation in meat products relies on a complex microbial community. Various strains of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) play crucial roles in fermentation. LAB ferment sugars into lactic acid, which lowers pH, creating an inhospitable environment for spoilage organisms. Understanding these microorganisms is essential in improving meat fermentation safety and achieving desirable flavors. Another critical player in meat fermentation is the yeast, which contributes to flavor enhancement and aroma development. A mix of indigenous and starter cultures is often utilized to control the fermentation process. The choice of microbial strains can significantly impact the flavor profile and physical characteristics of the final product. Additionally, molds can be beneficial in some processes, providing unique textures and surface characteristics. Traditional methods often incorporate naturally occurring microbial flora from the environment, allowing the meat to develop unique regional flavors. Over time, the interaction of these microorganisms with the meat matrix leads to complex biochemical transformations, contributing to the product’s flavor, aroma, and preservation. Overall, understanding the intricate microbial dynamics is vital in mastering the art and science of meat fermentation.
Temperature and humidity control are pivotal factors in traditional meat fermentation. These environmental conditions influence the growth rates of beneficial microorganisms and the chemical reactions taking place. Variations in temperature can lead to significant alterations in the quality and safety of fermented meat products. Generally, fermentation happens best at specific temperature ranges, allowing the LAB to flourish while preventing spoilage. Humidity levels also play a critical role, particularly in drying processes, as excessive moisture can lead to spoilage. Traditional fermentation techniques necessitate careful monitoring of these factors to achieve optimal results. For instance, many traditional recipes call for specific room temperatures and humidity levels to build the desired flavor profiles and textures. Additionally, fermentation time also varies based on the produced product and the desired characteristics. Some meats may require longer curing times for flavor development, while others may be ready in a shorter period. The artisan approach is predicated on the fermentation process, and each operator becomes attuned to the particularities of their environment. Thus, understanding these principles creates a foundation for mastering traditional fermentation methods.
Key Techniques in Traditional Fermentation
Numerous techniques in traditional fermentation of meat lead to a rich variety of flavors and textures. One common method is drying, wherein moisture is extracted from the meat. This process results in a concentrated flavor and prolongs shelf life. Air drying methods vary, including both hot and cold temperature applications. The smoking process can imbue meat with smokey flavors, often combined with other traditional spices or herbs. Additionally, spiced curing with salt is frequently used to enhance preservation, as salt draws moisture out from the meat, creating an environment resistant to spoilage. The incorporation of sugar can also aid in flavor building while feeding the fermentation microorganisms. Traditional preservation methods emphasize seasonal and regional ingredients, which leverage local flavors. Additionally, some traditional practices incorporate fermentation in conjunction with bread or starch, creating complex flavor interactions. The understanding of meat chemistry coupled with traditional practices yields delightful outcomes. Producers often serve these products alongside fresh accompaniments and local beverages, enriching the cultural experience associated with fermented meats. These authenticity-driven techniques create an immersive culinary narrative through which consumers explore the rich history of fermentation.
Health benefits associated with traditional fermented meats are gaining recognition alongside their consumption. The fermentation processes not only enhance flavors, but also contribute valuable nutrients. Probiotics formed during fermentation can bolster gut health, improving digestion and nutrient absorption. Some studies suggest that these beneficial microorganisms may also have immunomodulatory effects, promoting overall health. Furthermore, the fermentation process can enhance the bioavailability of certain vitamins and minerals, making nutrients more accessible to our bodies. Traditional fermented meats can be a source of high-quality protein, essential for a balanced diet. However, moderation in consumption is vital, as many fermented meats can be high in sodium. Strike a balance by enjoying these delicacies as part of a broader diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. Pairing fermented meats with fresh herbs, salads, or whole grains can enhance overall dietary health while providing balanced meals. Additionally, being aware of sourcing practices ensures quality and safety among fermented products. As consumers become increasingly health-conscious, recognizing the significance of traditional fermentation becomes essential in food selection and appreciation.
The Future of Traditional Fermentation
The future of traditional fermentation in meat products appears promising, intersecting innovation and heritage. Modern advancements in food science may bring insights into optimizing traditional methods while maintaining authenticity. The application of microbiome research can reveal valuable information regarding the microbes involved in fermentation. Understanding the mechanisms behind fermentation may enable the development of improved starter cultures that preserve traditional flavors. Furthermore, technological innovations such as sensor devices may aid in monitoring fermentation parameters with greater precision, thus ensuring safety and consistency. Culinary enthusiasts are increasingly engaging with heritage food practices, showcasing the demand for artisanal fermented meats in modern cuisines. Additionally, food sustainability trends encourage the resurgence of traditional meat fermentation methods, promoting local ingredients and responsible sourcing. More chefs and producers are creatively integrating fermented meats into contemporary dishes, bridging the gap between past and present. There exists an opportunity to educate consumers on the stories behind traditional methods, fostering appreciation for culinary heritage. As awareness of the health benefits of fermented foods grows, traditional fermentation stands to thrive as a fundamental aspect of not only preserving food but also cultivating cultural connections.
In conclusion, traditional fermentation methods in meat products elegantly combine art and science, resulting in flavors that tantalize the palate while nourishing the body. Fermentation is not merely a preservation technique but a historical practice steeped in culture and tradition. By understanding the intricate interactions of microorganisms and the careful crafting of techniques, we celebrate the rich diversity of fermented meats worldwide. Each regional variation tells a story that transcends time, connecting generations of artisans with modern enthusiasts. The meticulous attention to environmental factors, microbial communities, and psychological aspects will play a pivotal role in sustaining these traditions. As societal trends lean towards health-consciousness and sustainable practices, traditional fermented meats can find a revival in contemporary gastronomy. The challenge lies in perpetuating these methods while adapting to modern consumer preferences. Ultimately, fostering an appreciation for traditional fermentation enriches our culinary landscape and elevates our understanding of food. Makers and consumers alike carry the responsibility of preserving these practices for future generations while savoring the unique taste they bring to our tables. Embracing the art and science of traditional fermentation ensures that these age-old techniques continue to thrive.