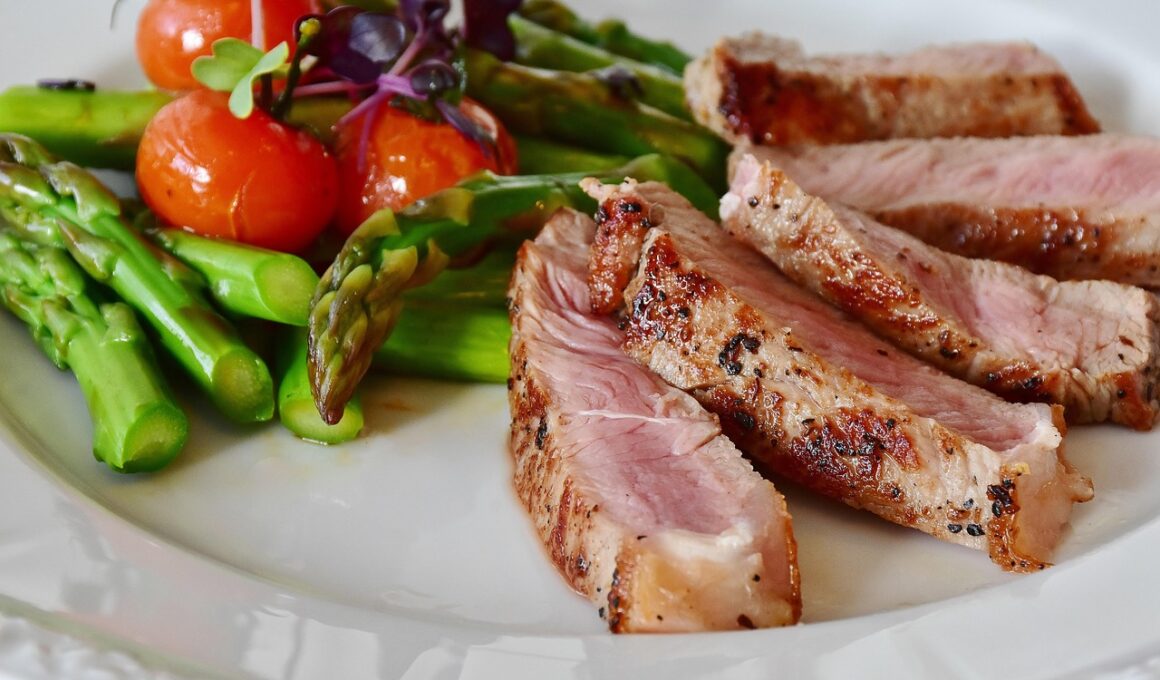
Low Carb Diet Variations and Their Effects: Insights from Recent Studies
Research on low carb diets has surged recently, revealing diverse approaches and their consequences on health. One significant study indicated that ketogenic diets predominantly lead to greater fat loss than traditional low-fat diets. Participants following a ketogenic diet experienced improved metabolic markers and enhanced energy levels. This dietary approach focuses on minimizing carbohydrates while emphasizing fats and proteins. However, it is essential to consider individual preferences and nutritional needs when adopting a low carb diet. Varieties include the Atkins diet, Paleo diet, and Mediterranean low carb versions, each offering unique benefits. For instance, the Mediterranean low carb emphasizes healthy fats from olives and fish, promoting heart health alongside weight management. Additionally, many reports suggest that low carb diets can result in better blood sugar control, beneficial for individuals with diabetes or metabolic syndrome. These diets may also reduce appetite, making it easier to adhere to strict dietary guidelines. Overall, low carb diets offer promising benefits but may require personalized adjustments to ensure sustainability and comprehensive health improvements over the long term.
Examining the Low Carb Diet Impact on Weight Loss
Recent studies emphasize the positive impact of low carb diets on weight management and fat loss. Individuals on these diets often report quicker initial weight loss compared to other dietary strategies. A significant reason behind this is the decrease in insulin levels, which facilitates fat breakdown and utilization for energy. Additionally, low carb diets can lead to reduced hunger pangs, allowing individuals to consume fewer calories effortlessly. Research indicates that participants on a well-formulated ketogenic diet lose weight consistently over time while maintaining muscle mass. This is crucial for overall health, as losing muscle can adversely affect metabolism. Variations such as the low-carb, high-fat (LCHF) diet have gained traction among fitness enthusiasts due to their effectiveness in promoting fat burning. Studies frequently highlight the role of dietary fiber in low carb plans, assisting digestion and enhancing feelings of fullness. The importance of high-quality food choices cannot be overstated; for effective weight control, whole foods should remain a priority. Although low carb diets could have temporary effects, long-term success often incorporates consistent lifestyle adaptations and ongoing support to sustain healthy habits over time.
Another feature of low carb diets is their potential mental health benefits, as identified in recent research. Many individuals on low carbohydrate regimens report enhanced mood, cognitive function, and decreased feelings of anxiety. This improvement may be attributed to stabilized blood sugar levels that reduce energy fluctuations throughout the day. Furthermore, ketones produced during a ketogenic diet have shown neuroprotective properties, potentially benefiting individuals with neurological disorders such as epilepsy. Interestingly, studies reveal a relationship between stable energy levels and better focus, making these diets appealing to those seeking improved cognitive performance. However, it is essential to approach these diets cautiously, as the initial transition phase can cause fatigue or irritability, commonly referred to as “keto flu.” Adequate hydration and electrolyte intake are vital during this period. As more evidence emerges, mental well-being continues to be a critical consideration for individuals contemplating low carb diets. Medical professionals advise evaluating personal mental health history and consulting a healthcare provider to tailor approaches appropriately, ensuring both physical and psychological needs are adequately addressed during dietary changes.
Low Carb Diets and Athletic Performance
Another area of growing interest is the effects of low carbohydrate diets on athletic performance. Recent studies have produced mixed results on whether these diets can enhance or hinder physical performance. Some athletes report improved endurance when adapting to ketogenic regimens, allowing the body to utilize fat stores for prolonged energy. Conversely, high-intensity workouts may be negatively impacted due to diminished glycogen stores, potentially leading to decreased strength and stamina. As a result, periodization becomes essential when incorporating low carb diets into an athlete’s meal plan. Certain strategies involve alternating low-carb phases with higher carb days to optimize performance. For example, endurance athletes may benefit from carb cycling, which fuels the body with carbohydrates on training days while adhering to low carb principles during rest periods. Additionally, recent research highlights the importance of combining adequate protein intake with low carb diets to support recovery and muscle retention. Ultimately, to understand individualized responses and conditions, athletes must prioritize monitoring their training performance alongside nutritional choices. Continuous adjustments can help create a balanced approach that improves physical outcomes in sports and endurance training while following a low carb diet strategy.
One appealing factor of low carb diets is their versatility, accommodating various lifestyles and preferences. People can adopt different low carb approaches that align with their dietary customs while reaping the benefits of reduced carbohydrate intake. The diversity within low carb diets is illustrated through the adoption of base principles from popular diets like Paleo and veganism, leading to interesting hybrids like vegan low carb variations. Recent studies have showcased the feasibility of plant-based low carb diets, arguing that they can offer nutritional adequacy while limiting calorie intake. However, individuals pursuing low carb vegan diets should pay extra attention to protein sources and essential nutrients, ensuring they consume foods rich in vitamins and minerals, such as legumes and nuts. Furthermore, the inclusion of adequate fats such as avocados and coconut can enhance flavor while providing energy. As diverse adaptations of low carb diets emerge, it is crucial for practitioners to consider necessary supplements to ensure they meet their nutritional requirements. The creative possibilities presented by low carb variations signify that it remains a popular choice among individuals pursuing health improvements and dietary satisfaction.
Low Carb Diets and Long-Term Health Effects
While numerous studies indicate short-term advantages of low carb diets, attention has also turned towards their long-term health implications. Comprehensive research is essential to elucidate the effects of prolonged carbohydrate restriction on various body systems. Some findings indicate improvements in cardiovascular health, with low carb diets showing a positive impact on cholesterol levels. People following low carb regimens frequently experience an increase in HDL (good) cholesterol and a drop in triglycerides, correlating with a lower risk of heart disease. However, potential concerns exist regarding the long-term sustainability of these diets and their influence on gut health. Prolonged carbohydrate restriction may lead to decreased fiber intake, which can impact proper digestion and gut microflora balance. Recent research emphasizes the importance of incorporating soluble and insoluble fibers even when limiting carbohydrates. Furthermore, the potential to develop nutrient deficiencies arises as low carb diets restrict many food groups. Emphasizing whole, nutrient-dense foods and conducting regular health checks will be fundamental for individuals pursuing long-term adherence to low carb diets. Awareness of these factors ensures individuals maintain health in both the short and long run.
As low carb diets capture the attention of healthcare professionals and the public, it is imperative to consider the importance of personalized dietary approaches. Each individual’s response to dietary changes varies, making it crucial to evaluate personal goals and health conditions prior to adopting such a diet. Collaborative discussions with healthcare providers and nutritionists can produce tailored strategies to ensure these diets meet unique needs without compromising overall health. It is essential to identify potential allergies and sensitivities to specific foods to optimize a low carb diet effectively. Personalized meal planning may incorporate local and seasonal foods, enhancing the diet’s appeal and supporting sustainable food choices. Beyond physical health, the inclusion of personal preferences, cultural practices, and enjoyment of meals should also be considered for long-term success. As the scientific literature on low carb diets continues to evolve, a balanced perspective will be vital in guiding individuals toward achieving health objectives responsibly. Ultimately, promoting sustainable practices and enhancing educational resources further empower individuals in their dietary adventures while navigating the world of low carb variations.