Prebiotics vs. Probiotics: Understanding the Difference
In the world of nutrition, prebiotics and probiotics play crucial roles in maintaining digestive health. Prebiotics are non-digestible food components that stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. They are typically found in high-fiber foods, such as bananas, onions, and garlic. By consuming prebiotics, individuals can enhance the population of good bacteria, like bifidobacteria. Improved gut health can lead to various benefits, including better digestion, enhanced immune function, and even improved mood. The key is that these substances serve as food for existing bacteria, allowing them to thrive. On the other hand, probiotics are live microorganisms, mainly bacteria, that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. Common sources include fermented products like yogurt and kimchi. They help balance the gut microbiota, especially after antibiotic use or during periods of stress. By understanding both prebiotics and probiotics, individuals can make informed nutrition choices to enhance their health. In the following sections, we will explore their differences in more detail, which is essential for optimal wellness.
The Role of Prebiotics
Prebiotics are often misunderstood; they are not live bacteria but rather the food that helps good bacteria to flourish. Key examples of these compounds are inulin and fructooligosaccharides (FOS). They play a vital role in enhancing the intestinal environment which, as a result, supports digestive health. Regular consumption of prebiotics can lead to increased production of short-chain fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties. These fatty acids are significant because they serve as an energy source for colon cells. They also aid in maintaining the gut barrier function, thus preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. Furthermore, prebiotics can enhance mineral absorption, notably calcium and magnesium. This is particularly beneficial for bone health. Many plant-based foods can be excellent sources of prebiotics. These include legumes, whole grains, and various fruits and vegetables. Incorporating these foods into your diet may lead to improved gut health and overall well-being. To achieve the best results, it’s recommended to include a variety of prebiotic foods, allowing for a diverse gut microbiome, which is key to optimal health.
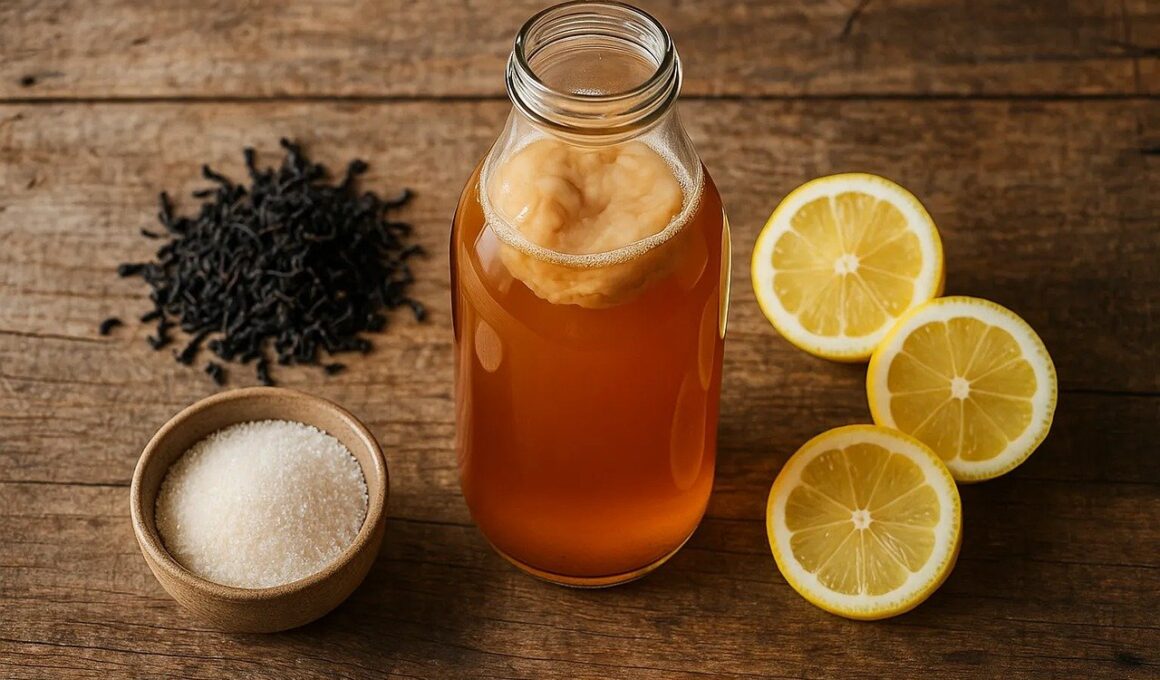
Probiotics, in contrast, are live microorganisms that have beneficial effects on health when consumed. They can be found in fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kombucha. Their primary role is to balance the gut flora, which can be disrupted by various factors such as antibiotics, poor diet, and stress. Regular consumption of probiotics is linked to numerous health benefits, including improved digestive health, enhanced immune function, and even mental health benefits. Studies show that certain strains of probiotics can alleviate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and diarrhea. Furthermore, probiotics work by competing with harmful bacteria for nutrients and space in the gut. Additionally, they can enhance the gut’s defensive barrier, thus reducing intestinal permeability. Candidates for probiotics include Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species, which can be incorporated into the diet through supplements or fermented foods. Choosing the right strain is crucial, as different strains have different effects and benefits. For those looking to improve their gut health, adding probiotics to the diet could be a practical choice.
Comparing Prebiotics and Probiotics
Prebiotics and probiotics are distinct yet complementary; understanding their differences can significantly impact your health. Prebiotics fuel the growth of bacteria already present in the gut, whereas probiotics introduce new beneficial bacteria. This synergy is essential for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome. It’s important to recognize that they do not perform the same functions. By consuming prebiotics, you’re supporting your existing gut flora, while probiotics help populate them with live bacteria. Both components work together, contributing to digestive wellness and overall health. Some foods naturally contain both, making it easier to incorporate them into a healthy diet. A common example would be yogurt with added fiber. However, not all probiotics contain prebiotic content, and vice versa. Therefore, consumers should strive for a varied diet rich in both prebiotics and probiotics. In doing so, they can significantly enhance their gut health and reap all the associated benefits. This holistic approach to nutrition can lead to significant improvements, making it easier to maintain good health in the long run.
Food manufacturers are increasingly recognizing the importance of prebiotics and probiotics, leading to the booming market of functional foods. These foods are designed not just for sustenance but also for providing health benefits. Beverages, bars, and dairy products now often boast added prebiotic fibers and live probiotic cultures. It’s essential for consumers to read labels carefully to ascertain just how much of these components are present. While some products claim to contain probiotics, the strains and quantities may not be adequate to confer health benefits. Education is critical when it comes to navigating the plethora of options available. In addition, it’s worth noting that individual responses to prebiotics and probiotics can vary widely; what works for one person may not work for another. Consulting healthcare professionals when considering these additions can ensure suitability and effectiveness. As interest within the nutrition field grows, more research is anticipated to better understand how these compounds interact within the body. Consumers should remain informed on the guidelines for dosages and types of strains that are most beneficial for their distinct health situations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Balance
Choosing the right balance between prebiotics and probiotics is essential for optimal health. Both elements contribute significantly to gut health, but achieving a harmonious balance is crucial for maximizing their benefits. Many healthcare professionals recommend a combination of both dietary sources. This can be done by incorporating various foods rich in prebiotic fibers alongside those that provide live probiotic cultures. Fermented foods, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables all offer pathways to enhance gut health. Additionally, keeping a regular dietary schedule can maximize the benefits derived from these nutrients. It’s advisable to start slowly, particularly with prebiotics, as they can cause digestive discomfort when introduced in excessive amounts. Likewise, varying the types of probiotics can aid in exposing the gut to diverse beneficial bacteria, important for gut diversity. This combined strategy may lead to improvements in digestive comfort, immune response, and overall well-being. In summary, understanding the roles of both prebiotics and probiotics, and employing them effectively in your diet, can dramatically enhance health outcomes.
As ongoing research delves into the impacts of prebiotics and probiotics on health, public interest continues to rise. With an increase in awareness comes the possibility of making better-informed decisions regarding dietary choices. Both prebiotics and probiotics are more than just passing health trends; they are backed by scientific evidence showing their importance in digestive and overall health. It’s always best to aim for a diet that is rich in whole foods, varied, and packed with the necessary components for a thriving gut microbiome. For those interested in exploring further, numerous resources, both online and offline, provide insight on how to effectively integrate these into your daily regimen. Staying educated on nutritional science can empower individuals to take charge of their health and well-being. Consumers should remain vigilant regarding the latest research findings to adapt their diets accordingly. In doing so, they can take proactive steps toward achieving and maintaining optimal health through effective use of prebiotics and probiotics. A balanced diet rich in diverse sources is key to unlocking the potential of these beneficial compounds.
In exploring prebiotics and probiotics, one must not overlook the impact of lifestyle choices. Regular physical activity, adequate hydration, and quality sleep can significantly influence gut health. These factors work synergistically with nutrition to create a balanced and thriving environment in the gut. Incorporating mindfulness practices, like stress management techniques, can also play a role in maintaining a healthy microbiome. The gut-brain connection reveals that mental health is closely tied to gut health, reinforcing the need for a holistic approach. Nutrition is undoubtedly foundational, but it is one piece of a larger puzzle. All these aspects combined lead to a healthy lifestyle, which can be incredibly beneficial for overall wellness. Consumers should aim to forge sustainable habits that promote good health. Practical steps include meal prepping with whole foods, staying hydrated, and treating oneself occasionally to refrain from feeling deprived. The ultimate goal is to create an enjoyable lifestyle that supports gut health and overall quality of life. With the right balance, individuals can enhance their well-being, fully leveraging the benefits that prebiotics and probiotics offer.