Top 10 Food Preservation Techniques to Extend Shelf Life
Food preservation is essential for maintaining the quality, taste, and safety of various food items. By employing effective preservation techniques, consumers can significantly extend the shelf life of their food products. Among the most common methods are refrigeration, freezing, dehydration, and canning. Each technique offers unique advantages, depending on the type of food and desired storage time. Moreover, understanding these methods allows people to minimize food waste, saving money and resources. Cooling food slows down the growth of harmful bacteria, while freezing suspends the activity of enzymes that can degrade food. Dehydration removes moisture, which inhibits microbial growth, and canning involves sealing food in airtight containers. Other effective approaches include pickling and fermentation, which not only preserve food but also enhance flavors. Vacuum sealing is another technique that can help preserve food by removing air, thus reducing oxidation. With thousands of food preservation strategies available, individuals can select the most suitable methods to apply based on their dietary needs and lifestyle.
1. Refrigeration
Refrigeration is one of the most accessible and widely practiced food preservation techniques. By maintaining a cool environment, refrigeration effectively slows down the growth of harmful bacteria, allowing fresh produce, dairy, and meats to last longer. Generally, keeping the refrigerator temperature below 40°F (4°C) is recommended, as this helps prevent spoilage. Fruits and vegetables typically last several days in a refrigerator, while cooked meals can be preserved for up to a week. It is crucial, however, to store food items in proper containers or bags to maintain their freshness. Moreover, avoiding overcrowding ensures a good airflow, further extending shelf life. It is also essential to regularly check for expired or spoiled items, as they can affect the quality of surrounding foods. Additionally, some foods, like tomatoes and bananas, shouldn’t be refrigerated, as their flavor and texture can deteriorate in cold temperatures. Therefore, understanding each food’s specific storage requirements is key to maximizing the benefits of this method of food preservation.
2. Freezing
Freezing is a highly effective method of food preservation, capable of significantly extending the shelf life of perishable items. Freezing halts bacterial growth, allowing food to remain safe and fresh for several months or even years when stored correctly. Enzymes responsible for spoilage and flavor degradation are also inactivated through freezing. Before freezing, it is advisable to blanch vegetables to maintain their color, texture, and nutrients. For best results, ensure the food is well-packaged in airtight containers or freezer bags to prevent freezer burn and off-flavors. When defrosting food, it is safety-critical to do so in the refrigerator or use the defrost setting on a microwave to avoid bacterial growth. Remember that some foods might change in texture once thawed, particularly fruits that contain high water content. For optimal flavor and quality, consume frozen items within specific timelines. Overall, freezing is an efficient food preservation strategy, especially for meal batch cooking, seasonal produce, and bulk purchasing.
3. Dehydration
Dehydration is the process of removing moisture from food to inhibit bacterial growth and spoilage. This method has been used for centuries to extend the shelf life of fruits, vegetables, herbs, seeds, and meats. By drying food, the concentration of nutrients, flavor, and texture can be enhanced, making it an excellent option for snacks, cereals, and trail mixes. Several techniques can be employed for dehydration, including air drying, sun drying, and using specialized food dehydrators or ovens. When using a dehydrator, ensure that the temperature settings maintain optimal flavor while effectively removing moisture. Proper packaging, such as vacuum sealing or airtight containers, is essential to preserve the dryness and longevity of dehydrated products. Store them in cool, dark places to prevent light and humidity degradation. Dehydrated foods can be stored for months or even years, maintaining their nutritional value if done correctly. Experimenting with different dehydrated fruits and herbs can add unique flavors to various recipes, creating versatile ingredients for culinary applications.
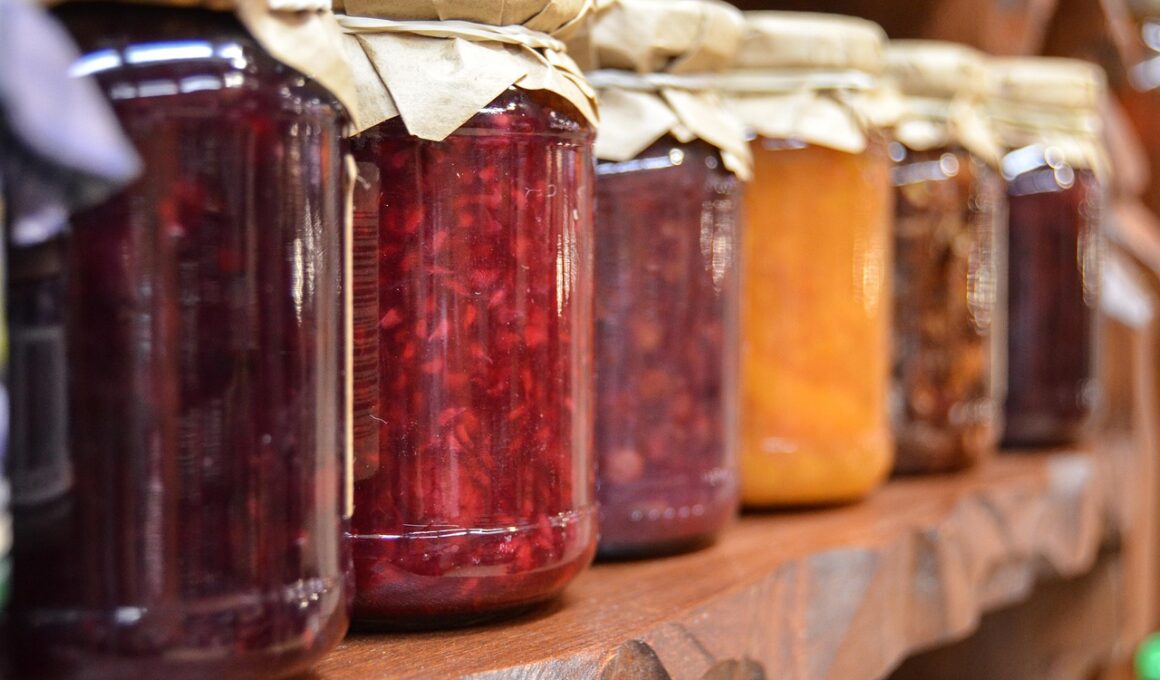
4. Canning
Canning is a popular food preservation method that involves sealing food in airtight containers, typically glass jars, to prevent bacterial growth and spoilage. This technique can preserve a wide range of foods, including fruits, vegetables, meats, and even sauces. The canning process typically consists of heating the containers to kill harmful microorganisms, allowing food to remain safe for months or years. There are two canning methods: pressure canning for low-acid foods and hot water bath canning for high-acid foods. Observing proper canning techniques, including sterilizing jars and following recipes, is critical to ensure food safety. Canned foods can be enjoyed at a later time without the need for refrigeration until opened, making it an efficient method of storage. While home canning requires attention to detail, it can be a fulfilling activity that preserves seasonal produce and minimizes food waste. Remember that once opened, canned goods should be refrigerated and consumed in a reasonable time frame. This longevity makes canning a valuable preservation strategy for households.
5. Pickling and Fermentation
Pickling and fermentation are ancient preservation techniques that transform foods while extending their shelf life. Pickling involves preserving food in an acidic solution, usually vinegar or brine, and is common with vegetables and fruits. This method not only prevents spoilage but also introduces unique flavors to the foods. On the other hand, fermentation utilizes bacteria or yeast to convert sugars into alcohol or organic acids, enhancing nutritional value. This process can be observed in products like sauerkraut, kimchi, and yogurt. Fermented foods come with added health benefits, such as improved digestion and enhanced gut health. Both methods allow for creative culinary expression, as various spices and flavorings can be introduced during the pickling process. The duration and technique used affect the final flavor and texture, allowing individuals to create personalized products. Stored correctly in jars, pickled or fermented items can last for months and may even improve with age. These methods provide interesting options for home cooks looking to enjoy delicious, preserved food while elevating their meals.
6. Vacuum Sealing
Vacuum sealing is an innovative food preservation technique designed to extend shelf life by removing air and sealing food in airtight bags or containers. This method reduces oxidation, a significant cause of spoilage, and helps retain flavors and nutrients for a longer period. Vacuum-sealed foods are perfect for sous-vide cooking, meal prep, and freezer storage. It is recommended to use a reliable vacuum sealing machine for optimal results and ensure that the bags are made from safe, food-grade materials. This technique is especially advantageous for bulk purchases, allowing you to purchase items in larger quantities without the risk of waste. Properly sealed foods can remain fresh in the refrigerator for weeks or months, compared to traditional storage methods. However, it is important to note that while vacuum sealing slows spoilage, it does not eliminate the risk of bacteria. Thus, it is recommended to combine vacuum sealing with other methods such as refrigeration or freezing for maximum effectiveness. Overall, vacuum sealing is a practical and efficient option for preserving food.
7. Use of Preservatives
The use of preservatives in food has gained attention due to their effectiveness in prolonging shelf life. These additives work by inhibiting microbial growth and spoilage, allowing food products to remain safe and palatable for an extended period. Preservatives are often categorized as natural or synthetic. Natural preservatives include salt, sugar, vinegar, and certain herbs, while synthetic options encompass chemical preservatives. The choice of preservatives heavily relies on the type of food and desired shelf life. For instance, salt is a common preservative used in curing meats and vegetables, while citric acid is prevalent in beverages and canned goods. While preservatives are generally considered safe for consumption, it is essential to stay informed about their impact on health and to seek cleaner alternatives whenever possible. Monitoring food labels allows consumers to make better choices concerning their food quality. Understanding which preservatives are being used can encourage consumers to explore cleaner eating habits. This can ultimately lead to healthier lifestyles and less reliance on processed foods.