The Connection Between Gut Health and Allergies
The relationship between gut health and allergies is a complex interplay that has garnered significant attention in recent years. The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses, which can have a direct impact on allergic reactions. When gut health is compromised, the balance of beneficial and harmful bacteria can shift, leading to an overactive immune system. This dysbiosis is thought to contribute to the development of food allergies, environmental allergies, and even asthma. Research suggests that children with a diverse gut microbiome are less likely to develop allergies, underscoring the importance of gut health from an early age. Furthermore, foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can promote a healthy microbiome and may help alleviate allergy symptoms. Additionally, probiotics are being investigated for their potential to enhance gut health and strengthen the immune system, potentially diminishing allergic responses. Understanding this connection emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to health, focusing not only on avoiding allergens but also on nurturing gut flora for overall wellbeing and resilience against allergies.
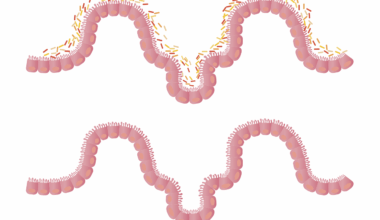
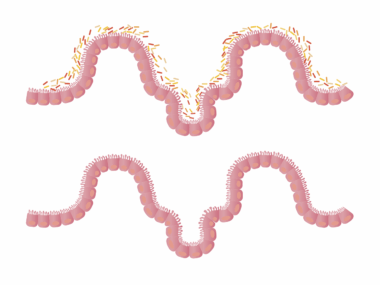
In addition to diet, stress and lifestyle factors also play a significant role in gut health, which can indirectly affect our allergic responses. Chronic stress has been shown to alter gut permeability, often referred to as “leaky gut syndrome.” This condition allows toxins and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream, triggering allergic reactions in susceptible individuals. Engaging in stress-reducing practices, such as yoga, meditation, or mindfulness, can improve gut health and, consequently, reduce allergy symptoms. Furthermore, a balanced lifestyle that includes regular physical activity can positively influence gut microbiota. Exercise has been linked to increased diversity in gut bacteria, which is vital for good immune function. Also, staying hydrated and maintaining a regular sleep schedule can further support digestion and overall gut health. By incorporating these lifestyle changes, individuals can take proactive steps toward maintaining a healthy gut environment, potentially reducing their risk of developing allergies. Holistic health strategies that address both gut and overall wellbeing can lead to improved quality of life and reduced health complications associated with allergies, creating a comprehensive solution to these complex issues.
The Importance of Probiotics
Probiotics, which are live beneficial bacteria, have gained popularity as a supplement aimed at improving gut health. These microorganisms help restore the balance in the gut microbiome by promoting the growth of healthy bacteria, effectively combating dysbiosis. Numerous studies suggest that incorporating probiotics into the diet can bolster the immune system, thus aiding in the prevention of allergies. More specifically, they may play a role in the development of tolerance to allergens, particularly in infants and children. Probiotic-rich foods include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, which can be easily integrated into a regular diet. For those unable to consume these foods, probiotic supplements offer a convenient alternative. However, it is crucial to choose high-quality, clinically-tested strains that have been proven effective in allergy reduction. Additionally, the timing of probiotic introduction matters; research indicates that early supplementation may be more beneficial in providing long-term allergy protection. While it is essential to remember that individual responses to probiotics may vary, the potential benefits of these supplements for gut health and allergy management warrant further exploration and consideration.
The role of prebiotics should not be overlooked when discussing gut health and allergies. Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria, promoting their growth and activity. By supporting the microbiota’s health, prebiotics can indirectly influence immune responses and improve overall gut function. Foods high in prebiotics include garlic, onions, asparagus, and bananas, which can easily be incorporated into everyday meals. A diet high in prebiotics not only enhances gut health but may also help reduce the severity of allergic reactions. Emerging research indicates that a well-fed gut microbiome contributes to a more balanced immune system, decreasing the likelihood of overreactions to allergens. Furthermore, a blend of both probiotics and prebiotics—often referred to as synbiotics—can be particularly beneficial. This synergistic effect enhances the growth of friendly bacteria while simultaneously providing their food source. Ultimately, fostering a gut environment rich in prebiotics can play a pivotal role in managing allergies and, consequently, in improving long-term health outcomes and quality of life for those affected by allergy-related issues.
Food and Allergies
Dietary choices can greatly influence gut health, which in turn affects the body’s allergic responses. Specific foods have been shown to either support or hinder gut microbiome health, leading to varying effects on allergies. For instance, diets high in processed foods, sugars, and saturated fats can harm gut bacteria, promoting inflammation and possibly triggering allergic reactions. Conversely, a diet rich in whole, natural foods, including anti-inflammatory options like fatty fish, nuts, and leafy greens, can nurture gut flora. Foods rich in antioxidants, like berries and citrus fruits, can also mitigate inflammation. Furthermore, keeping a food diary can help individuals identify patterns between their diet and allergy symptoms. Eliminating potential allergens, such as gluten, dairy, or common triggers, may offer symptom relief. Additionally, considering food combinations and preparation methods can maximize nutrient absorption and therefore, gut health. Understanding the impact of different foods can empower individuals to make informed choices about what to consume or avoid, ultimately assisting in allergy management and improving gut health holistically. These dietary strategies can empower individuals to take control of their health outcomes, especially concerning allergies.
Seasonal weather changes can also affect gut health, making the management of allergies more complex. For example, during springtime, pollen counts rise, and many individuals suffer from seasonal allergies. This increase in allergens can create additional stress on the immune system, particularly when gut health is compromised. Environmental toxins and pollutants can further exacerbate these issues. To address these concerns, individuals can adopt strategies to support their gut during high pollen seasons. Consuming foods known to help combat inflammation, such as turmeric and ginger, can bolster immunity. Staying hydrated is important, as it helps in flushing out toxins and supporting the digestive process. Utilizing air purifiers indoors can minimize allergen exposure and promote a cleaner environment. Furthermore, maintaining a regular schedule for meals and sleep during peak allergy seasons can support gut health amidst external stressors. Understanding the correlation between environmental factors and gut health can empower those affected by seasonal allergies to take proactive measures that enhance their overall health and wellness during challenging times, allowing for better management of allergy symptoms.
Gut Health and Long-Term Wellness
Ultimately, it becomes evident that a robust connection exists between gut health and the management of allergies, emphasizing the need to prioritize this often-overlooked aspect of overall wellness. Making informed dietary and lifestyle choices can create a supportive environment for gut microbiota, which can subsequently strengthen immune responses and reduce the severity of allergies. Embracing practices such as regular exercise, stress management, and supplementation with probiotics and prebiotics is essential. Education about the importance of gut health in relation to allergies can lead to a significant reduction in personal suffering and enhance one’s quality of life. Individuals are encouraged to consult healthcare professionals to create tailored plans that support their unique health needs. As research continues to evolve, our understanding of the gut-allergy connection will deepen, allowing for more effective preventive strategies and treatments. The path toward holistic health encompasses taking steps that focus on nurturing the gut microbiome while also addressing allergy triggers. In conclusion, proactive efforts to improve gut health can transform wellness and establish a foundation for long-term health free from the burdens of common allergies.
In summary, recognizing the intimate relationship between gut health and allergies opens up new pathways for holistic health approaches. By prioritizing gut health, individuals can enhance their immune response and mitigate pesky allergic reactions. This understanding invites a more integrative view of health, where gut microbiome management becomes part of daily wellness routines. Emphasizing the significance of nutritious foods, stress reduction techniques, and mindful lifestyle practices will lead to optimal gut function. Moreover, the role of probiotics and prebiotics should be embraced as a powerful ally in allergy management. Staying informed about emerging research can empower individuals to make sound health choices. As our knowledge continues to expand, the solutions for managing allergies will evolve, paving the way for innovative therapies that target gut health. Through personalized approaches and community support, those affected by allergies can find relief, improving their quality of life significantly. Investing in gut health has the potential to create a cascade of benefits, enhancing overall wellbeing and minimizing the impact of allergies. This holistic perspective shifts the focus from merely treating symptoms to understanding the underlying causes and creating lasting solutions for a healthier future.