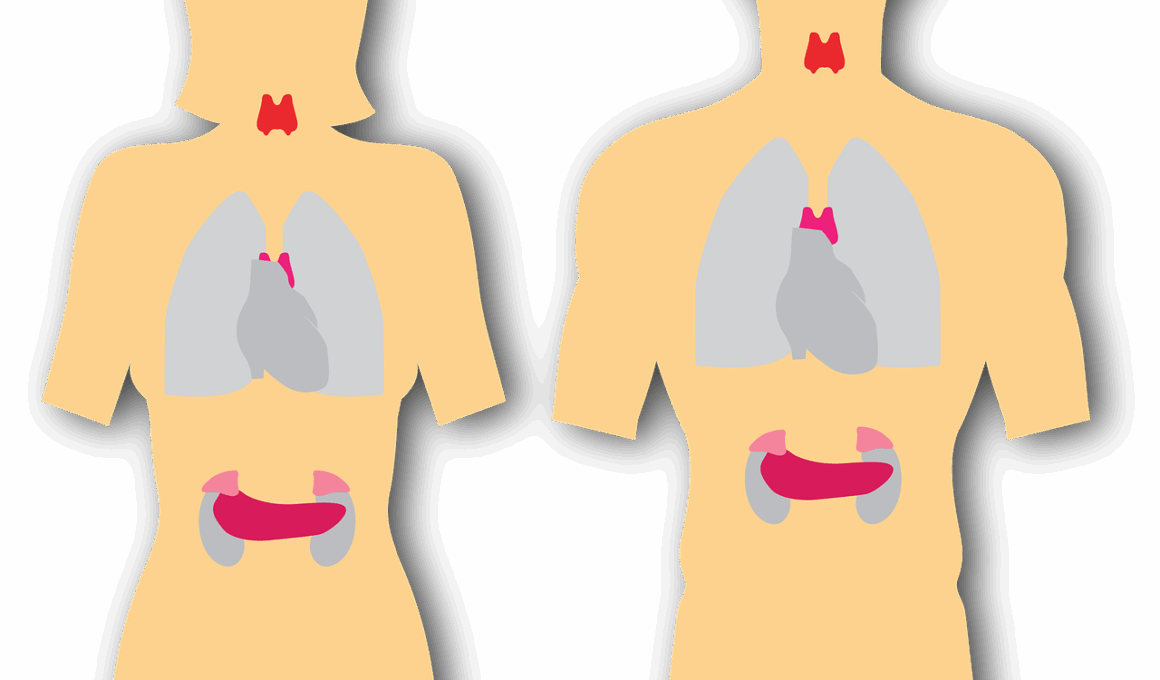The Connection Between Gut Health and the Endocrine System
The endocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and mood. It is made up of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream, influencing distant organs and systems. One of the less discussed factors that significantly impacts our endocrine health is the gut microbiome. The gut houses trillions of microorganisms, which interact with the immune and endocrine systems. This intricate relationship means that gut health can directly affect hormonal balance. For instance, a healthy gut can enhance hormone production and balance, while an unhealthy gut can lead to hormonal disruptions. Understanding this connection is essential for individuals looking to optimize their hormonal health. Many people often overlook gut health, focusing solely on dietary choices or exercise routines. However, improving gut health should be part of a comprehensive approach to maintaining hormonal wellness. Dietary changes, probiotics, and lifestyle adjustments are some strategies that may positively influence both gut microbiota and endocrine function. Therefore, awareness of the gut-endocrine link equips individuals with tools for managing hormone-related health issues and enhancing overall well-being.
Your gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem, impacted by diet and lifestyle factors. The balance of good and bad bacteria in the gut can directly influence the production and regulation of hormones such as cortisol and estrogen. For instance, consuming a rich diet filled with fiber and fermented foods supports beneficial gut bacteria growth. In contrast, high sugar and processed food intake can foster detrimental bacteria, leading to gut dysbiosis. The symptoms of hormonal imbalances caused by gut health issues can vary widely, from fatigue and weight gain to mood swings and digestive problems. Addressing these symptoms often involves targeting the gut health directly. Furthermore, recent research indicates that specific gut bacteria can produce short-chain fatty acids, which play a vital role in hormone signaling. This highlights that the food you eat not only nourishes your body but also shapes your hormonal landscape. Therefore, recognizing the foods that restore and maintain gut health is paramount for balancing hormones and improving endocrine health. An integrated approach incorporating both gut and hormonal health can lead to sustainable well-being and vitality across a lifespan.
The Impact of Gut Microbiota on Hormonal Health
The relationship between gut microbiota composition and hormonal health cannot be overstated. Certain beneficial bacteria in the gut can synthesize essential nutrients, such as vitamins and certain minerals, aiding hormone production. For example, B vitamins play a crucial role in hormone synthesis and regulation. Thus, a healthy gut can contribute to an effective endocrine response by ensuring adequate nutrient availability. Additionally, gut bacteria are involved in the metabolism of steroids, such as testosterone and estrogen. By altering the metabolism of these hormones, gut microbiota can directly impact hormonal balance. Disruptions in this balance can lead to a range of health issues, including polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women and reduced testosterone levels in men. This highlights the need for regular assessments of gut health, particularly in patients exhibiting hormonal imbalance symptoms. Interventions like promoting healthy dietary habits, reducing stress, and incorporating probiotics may positively impact gut health and hormone function. It’s vital to adopt a holistic view that acknowledges the interdependence of gut health and endocrine function as we strive toward optimally functioning bodies.
Moreover, chronic stress can profoundly affect both gut health and the endocrine system. Stress often leads to increased cortisol levels, which can adversely affect gut bacteria diversity. This can create a vicious cycle—imbalanced gut bacteria can cause inflammation and further hormonal disruption, perpetuating stress levels. Managing stress through mindful practices, such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises, can promote a healthier gut microbiome. Creating a resilience to stress not only benefits endocrine health but also enhances overall gut function and health. Furthermore, understanding the mind-gut connection reinforces the need for a supportive environment that nurtures both physical and emotional well-being. Music therapy, spending time in nature, or engaging in hobbies can create positive vibrations that support hormonal and gut health. By addressing stress as a significant factor in personal health journeys, individuals can enhance their hormonal balance. In conclusion, integrating stress management techniques along with dietary and lifestyle choices fosters a healthier relationship between the gut and endocrine systems. Emphasizing these connections can empower individuals in their quest for holistic health.
Nourishing Your Gut for Endocrine Balance
The foods you consume play a critical role in nurturing both your gut health and hormonal balance. Diets rich in whole foods, particularly fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, have been shown to support a healthy microbiome. Specifically, fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut can enhance beneficial gut bacteria, directly influencing hormonal regulation. Including a variety of antioxidants and fiber-rich foods can also promote gut health. Gut health fosters the production of hormones that are vital for energy levels, mood stabilization, and metabolism. On the contrary, processed foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats can encourage the growth of harmful bacteria, leading to potential endocrine disruption. Implementing a diverse diet, rich in prebiotics and probiotics while being mindful of food quality, can produce remarkable changes in both gut health and hormonal balance. Additionally, staying hydrated is essential, as water aids digestion and nutrient absorption. Thus, dietary awareness should be a key consideration for anyone aiming to achieve optimal hormonal health through gut optimization.
Regular physical activity is another essential guardian of gut and endocrine health. Engaging regularly in exercise can improve gut mobility and promote favorable changes in gut microbiota composition. Activities like aerobic exercises and strength training also help maintain a healthy weight, which plays an essential role in hormonal balance. Weight fluctuations can lead to increased levels of stress hormones, negatively affecting the gut microflora and further disrupting hormone levels. Furthermore, incorporating various forms of exercise can create physical and mental benefits, promoting both physical health and emotional well-being. Prioritizing movement not only enhances gut health but also supports mental health and stress management. Thus, a holistic approach that integrates physical activity into daily routines can be pivotal. Vibrant energy levels, well-regulated hormones, and improved digestive health form a synergistic relationship through exercise. The importance of staying committed to a physically active lifestyle cannot be understated; it strengthens not only the body but the intricate connections between the gut and the endocrine system.
The Future of Hormonal Health Management
Looking Forward, integrating gut health into conventional hormonal health management is vital for a more holistic view of health. Personalized nutrition and microbiome analysis can potentially lead to tailored interventions focusing on gut health for better endocrine regulation. Future research may unveil even deeper connections between gut microbiota and hormonal health, offering insights into previously unexplored dimensions of treatment. The ongoing exploration in this area may reframe how we view conditions traditionally seen solely from a hormonal perspective. By implementing strategies rooted in gut health optimization, we can effectively address various hormonal issues that plague many individuals today. This convergence can encourage practitioners to adopt a more integrative approach in their clinical practices, focusing on a lifestyle-centered framework. Innovative therapies that combine diet, exercise, and targeted supplements are on the horizon, promising better recovery times and health outcomes. As we advance our understanding, individuals will become increasingly empowered to take charge of their gut health, which directly influences endocrine function. The future of hormonal health will lie in the fusion of traditional healthcare with innovative gut-centered approaches, delivering beneficial outcomes for overall health.
In summary, the connection between gut health and the endocrine system is profound and multifaceted. Hormonal balance is intricately tied to the health of our gut microbiome, impacting everything from mood to metabolism. The importance of understanding this relationship can guide individuals toward more comprehensive health strategies. Incorporating dietary improvements, stress management techniques, physical activity, and awareness of gut health can create a harmonious balance that nurtures both systems. As research surfaces, the synergy between these two vital aspects of health will only become clearer. It empowers individuals to make informed choices that positively influence their hormonal wellness. Addressing gut health is thus paramount in a holistic approach to endocrine health. By highlighting how interconnected our systems are, we open doors to enhanced health outcomes and improved well-being. Envisioning a healthier future involves not just the focus on hormonal treatments but also embracing the power of gut microbiota. Let us move forward embracing a comprehensive approach; optimizing both gut health and hormonal balance can lead to thriving. Everyone deserves a chance at improved health and quality of life, and understanding their interconnectedness is the first step in that journey.