Managing Medication and Diet for Optimal Congenital Heart Health
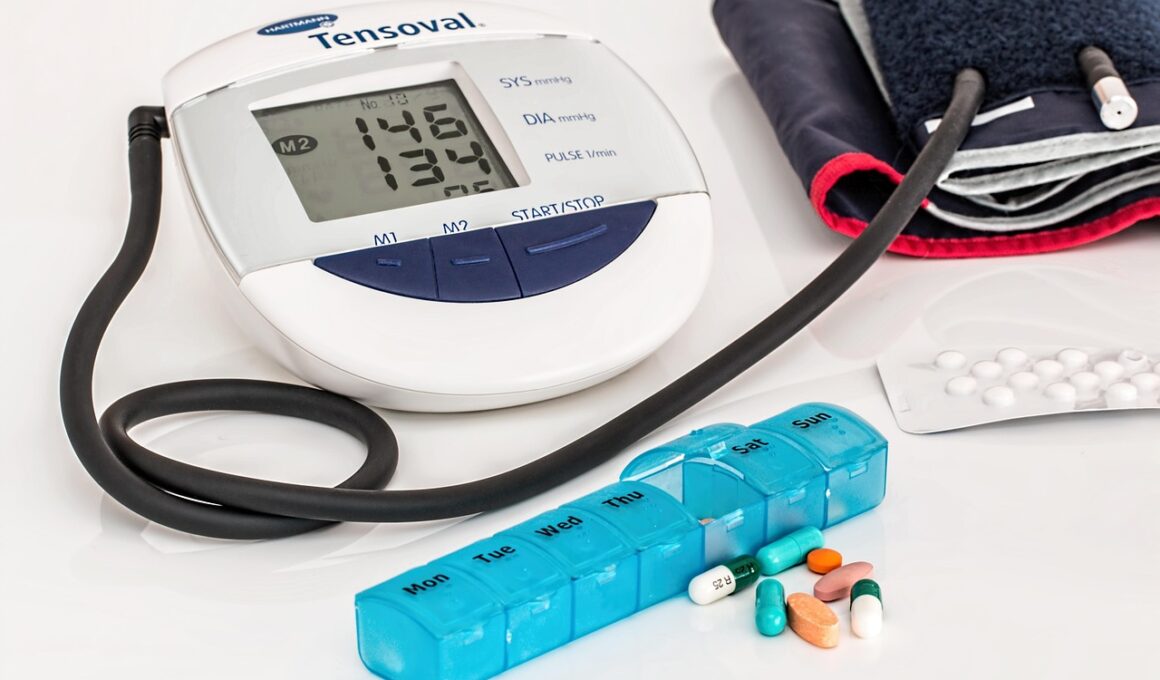
Congenital heart defects (CHDs) present unique challenges when it comes to heart health management. Patients often require a tailored approach to medication and dietary adjustments to maintain overall well-being. Understanding the prescribed medications is vital for successful management. Some common medications for CHDs include diuretics, anticoagulants, and beta-blockers, among others. Adhering to the prescribed medication regimen helps in controlling symptoms and preventing complications. It’s essential for caregivers to monitor the patient’s response to medications and communicate any concerns with healthcare providers. Regular check-ups are crucial to reassess medication needs as the patient’s condition evolves. Education about potential side effects can empower patients and caregivers to identify issues promptly, enabling timely interventions. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet plays a significant role in supporting heart health. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can promote cardiovascular health and overall fitness, assisting in weight management. Consider consulting a registered dietitian specializing in heart disease to create a personalized meal plan appropriate for managing congenital heart defects.
Effective dietary management can significantly impact the quality of life for individuals with congenital heart defects. Patients and caregivers should be mindful of sodium intake as excessive sodium can lead to fluid retention, exacerbating heart-related issues. Incorporating potassium-rich foods, such as bananas and spinach, can help balance sodium levels and support heart function. The incorporation of omega-3 fatty acids from sources like fatty fish or flaxseeds may reduce inflammation and support overall cardiovascular health. Avoiding processed foods, which often contain hidden salts and unhealthy fats, is crucial for maintaining optimal heart health and minimizing complications related to congenital heart defects. Educating individuals and families about reading nutrition labels can enhance their ability to make informed dietary choices. Additionally, it is essential to stay hydrated, but fluid intake should be monitored under medical guidance, especially for those with significant heart issues. Cooking at home can empower patients, allowing them to control ingredients and maintain healthy eating patterns. Participating in community cooking classes may also foster social support and help build camaraderie among families dealing with similar challenges related to congenital heart defects.
Promoting Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes play a substantial role in managing congenital heart defects effectively. Engaging in regular physical activity is essential; however, patients must work with their healthcare teams to determine appropriate exercise levels. Gentle activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can enhance cardiovascular health and improve overall stamina. Gradual increases in activity are recommended to avoid undue strain on the heart. Beyond physical activity, maintaining a healthy work-life balance can promote emotional well-being and decrease stress levels, contributing positively to heart health. Practicing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness or yoga, can also be beneficial for emotional regulation. One should prioritize sufficient sleep as inadequate rest can affect heart health negatively. Establishing a consistent bedtime routine can help improve sleep quality and support recovery and healing. Encouraging family members to engage in healthy lifestyle changes can foster a supportive environment, helping individuals adjust more effectively. Offering joint social activities centered on fitness can not only bring families together but also create opportunities for those with congenital heart defects to lead healthier lives collectively.
Regular monitoring of heart health is essential in managing congenital heart defects. Routine check-ups with healthcare specialists, including cardiologists, ensure that any complications are detected early. Patients should keep track of their symptoms, medication adherence, and daily activities, documenting any changes in their condition. This information can be invaluable during medical consultations, providing concrete data that can inform treatment adjustments. Telemedicine options can also enhance access to specialists, particularly for those in remote areas or with mobility limitations. Understanding the importance of routine diagnostic tests, such as echocardiograms and EKGs, will help patients and families stay proactive in managing their heart health. Being informed about upcoming procedures and interventions allows families to prepare mentally and logistically. Educating patients about the uniqueness of their condition can empower them and their families to take an active role in their healthcare management. Building a collaborative relationship with healthcare providers will encourage open communication, ensuring that patients feel more confident addressing any questions or concerns regarding their treatment and lifestyle choices.
Empowerment Through Education
Education is a critical component in managing congenital heart defects effectively. Resources such as workshops, webinars, and support groups can provide valuable information to patients and families. Connecting with other families facing similar challenges can reduce feelings of isolation and provide practical insights on managing daily life with congenital heart defects. There’s a wealth of online resources that can supplement this education, offering expert advice on medication management, diet, and lifestyle changes. For instance, organizations like the American Heart Association provide comprehensive guides and information focused on heart health tailored to different conditions. Using social media platforms opens avenues for sharing experiences and gaining new perspectives from those navigating the same journey. Patients and families should discuss findings with healthcare providers to ensure that the information is accurate and applicable to their unique situations. Customized education on any new advances in treatment options, medications, or dietary recommendations can empower patients. This knowledge equips families to advocate for their health effectively, contributing positively to their overall well-being and heart health management.
In addition to understanding medication and diet, managing congenital heart defects necessitates addressing psychological aspects. Individuals may experience anxiety or depression related to their health conditions; hence, mental health support is essential. Psychologists or counselors specializing in chronic illness can help patients develop coping mechanisms for emotional challenges they encounter. Families can benefit from education regarding the psychosocial effects of congenital heart defects, promoting empathy and support within the household. Open discussions about fears, expectations, and day-to-day challenges may foster emotional resilience among individuals. These conversations can offer insights into how the condition impacts family dynamics, which may adjust expectations or create additional means of support. Encouraging patients to express their thoughts and feelings can be instrumental in navigating their healthcare journey. Furthermore, resilience-building strategies can aid children and adolescents in adapting to their health realities over time. Schools can also play a pivotal role by creating environments where young individuals with congenital heart defects feel understood and supported, contributing to their emotional and psychological well-being.
Conclusion
Managing congenital heart defects requires a multidisciplinary approach to ensure optimal heart health throughout a patient’s life. Collaboration among medical professionals, families, and patients enhances the effectiveness of treatment and lifestyle interventions. As awareness rises about the importance of diet and medication management, families are better prepared to advocate for their loved ones. Incorporating therapeutic lifestyle changes and fostering healthy habits can create a supportive network, ultimately promoting heart health. The journey may be challenging, but empower patients through education, emotional support, and resilience. It’s essential to celebrate progress, however small, and recognize the strengths that arise from managing congenital heart defects. Regular follow-ups should feel collaborative rather than burdensome and provide opportunities for personal growth and improvement. Whether through sharing experiences or relying on community resources, patients and their families can foster hope and connection amid this journey. As we continue embracing advancements in medical science and promoting healthy lifestyle choices, the future remains hopeful for those managing congenital heart defects. Together, we can create an environment conducive to optimal heart health for everyone involved.
In conclusion, individuals affected by congenital heart defects can lead fulfilling lives with proper medication adherence, a balanced diet, and emotional support. Continuous education and communication with healthcare providers are key factors in successfully managing heart health. Through collaborative efforts, families can create strategies to adapt to ongoing changes that come with healthcare needs. Appreciating the importance of self-care and reinforcing healthy habits among family members will bolster overall well-being. The commitment to understanding and supporting one another is foundational as we navigate the complexities of congenital heart defects together. By prioritizing heart health and remaining vigilant in pursuing the best resources, patients create a positive impact on their health outcomes. Living with congenital heart defects may require adaptation, but it must not define one’s quality of life. Each individual has the potential for growth, happiness, and resilience in the face of challenges. Continued awareness, research, and community involvement can drive progress in support of congenital heart defects management. Ultimately, every step taken towards optimal heart health contributes to a brighter future for those affected by congenital heart defects.